
打印出來prompt如下:

在input側,mistral-nemo的做法是直接將用戶提供的tool schema轉為string,并包裹在特殊的tag(AVAILABLE_TOOLS)之中,然后插入到user query之前。
既然都是組裝Prompt,我們拿它和Kor的Prompt做個對比:
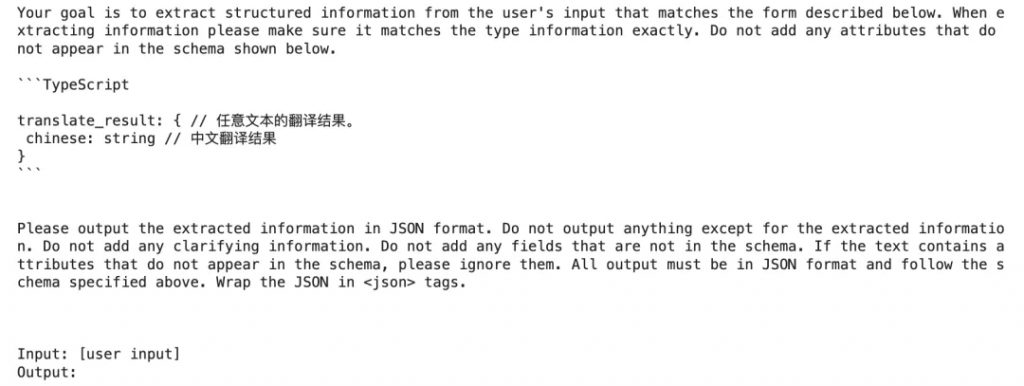
可以發現,mistral-nemo的prompt更精簡(不包含Your goal is …. 、All output must be in JSON format…. 等內容)。
接著,我們來看output側。
mistral-nemo的輸出結果如下:
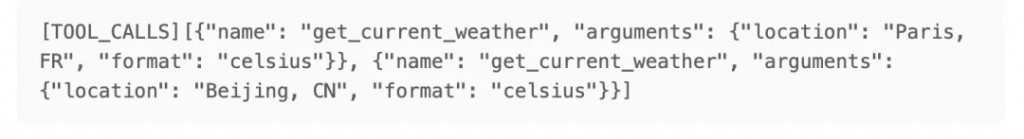
看起來,這是一個普通的text generation過程,通過特殊標記(TOOL_CALLS)來表明,這是一個tool_call message,而非常見的text message;同時nemo支持同時call多個tools,每個call為一個字典,其中包含function name和arguments參數(json格式)。
總結一下,mistral-nemo這樣實現FC:
通過分析mistral-nemo,可以猜測,各家LLM公司有自己的FC prompt template,既體現在input側,也體現在output側。
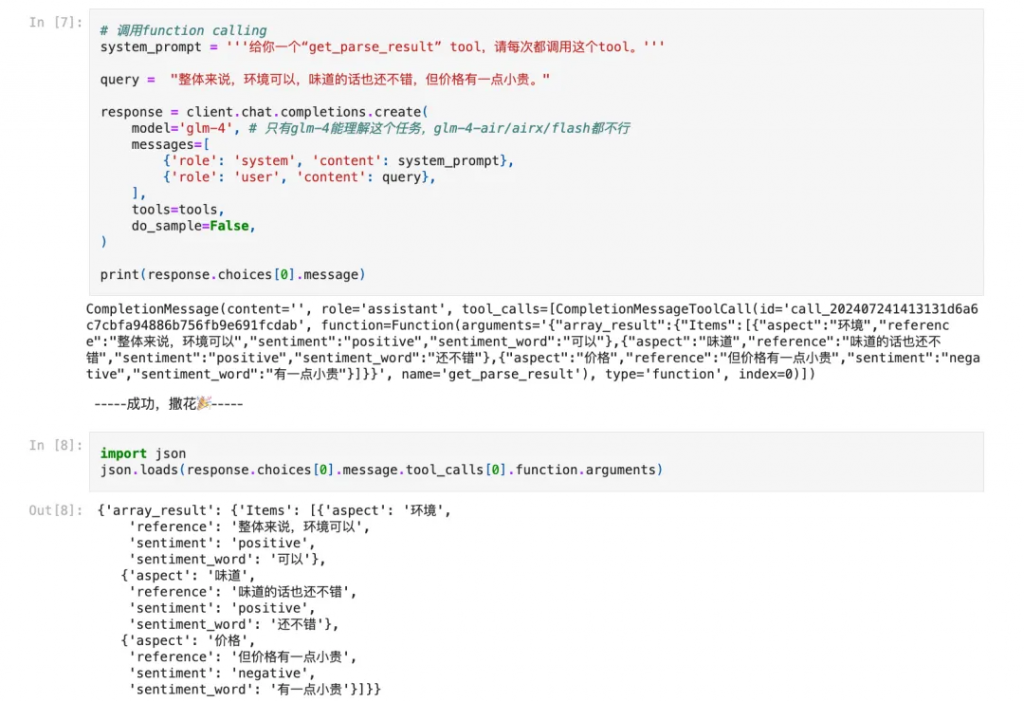
動手實踐是學習的好方法,本期我們仍然選用第一期的2個練習(中文翻譯器、評價解析)。
練習部分的所有代碼,都已整理在下方git,建議讀者實際運行代碼來學習:
https://github.com/duanyu/structured_generation_with_llm/blob/main/Lecture2_Function_Calling.ipynb
考慮到排版,筆者直接將截圖貼在下面。
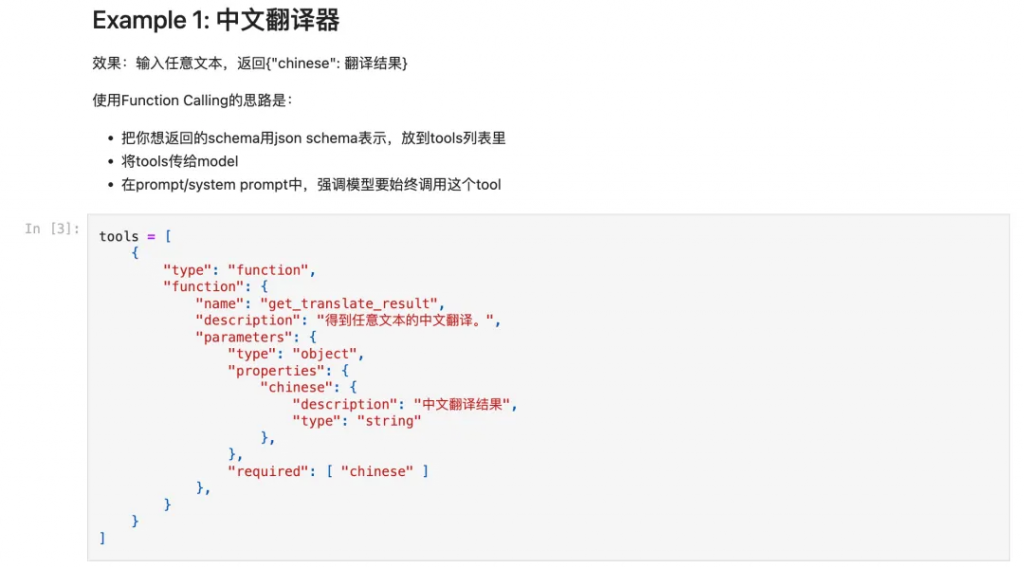
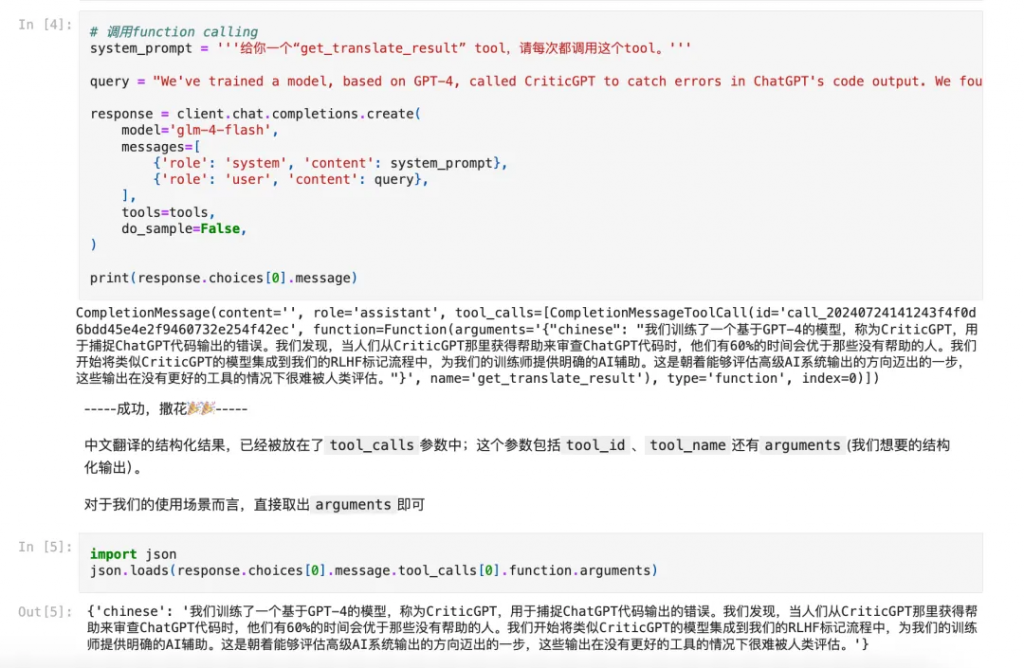


本文介紹了第二種進行Structured Generation的技術:Function Calling。FC是Agent的基石,structured generation則是“副產品”;讀者在實際使用中,可以將FC與Kor(或者自己寫的prompt)做對比,選擇效果更好的方案。
需要提到的是,FC雖然經過了fine-tuning,輸出結構的穩定性有一定保證,但若未使用constrain decoding技術,那么仍然不是100%魯棒的;同時,筆者在練習中發現,當使用glm-4-flash/air/airx模型時,FC難以有效加入few-shot examples,但在第一期練習中,glm4-9b-chat + Kor對few-shot examples十分友好,這可能是FC的一個問題(但也可能是用法不對,歡迎有經驗的讀者指正)。
文章轉自微信公眾號@漫談NLP